Pemphigus vulgaris
Pemphigus vulgaris is a rare long-term condition caused by a problem with the immune system. It causes blisters in the mouth and on the skin. It can be very serious, but treatment can help control it.
Symptoms of pemphigus vulgaris
Pemphigus vulgaris causes blisters that burst easily and leave very sore patches.
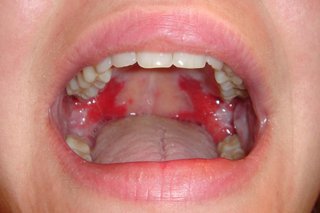
ISM/SCIENCE PHOTO LIBRARY: https://www.sciencephoto.com/media/1232728/view
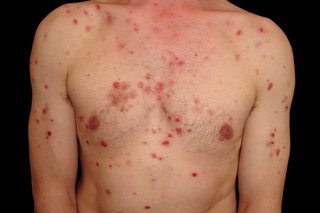
ISM/SCIENCE PHOTO LIBRARY: https://www.sciencephoto.com/media/1232726/view
If you're not sure it's pemphigus vulgaris
Pemphigus vulgaris can have similar symptoms to more common conditions, such as impetigo and hand, foot and mouth disease.
Do not try to diagnose yourself. See a GP if you're worried.
Non-urgent advice: See a GP if:
- you have blisters or sore patches in your mouth or on your skin that do not go away or keep coming back
Treatments for pemphigus vulgaris
If a GP thinks you could have pemphigus vulgaris, they can refer you to a skin specialist (dermatologist) for tests and treatment.
Blisters caused by pemphigus vulgaris usually come and go over time. There's no cure, but treatment can help.
The main treatments are:
- steroid tablets
- other medicines such as azathioprine, methotrexate and rituximab
It usually takes a few weeks for the blisters to heal. Once this happens, you'll probably need treatment for several years to help stop the blisters coming back.
It may be possible to stop treatment eventually. If the blisters come back, you may need to repeat treatment.
Things you can do if you have pemphigus vulgaris
If you have pemphigus vulgaris, there are some things you can do to help ease the symptoms and reduce the risk of further problems.
Do
-
clean your teeth using a soft toothbrush and mint-free toothpaste
-
use antiseptic or painkilling (anaesthetic) mouthwash (try to avoid mouthwashes that contain alcohol)
-
keep any sore patches clean to reduce the risk of infection
-
have regular dental check-ups
Don’t
-
do not eat spicy, acidic or hard foods if you have blisters in your mouth
-
do not do activities that could damage your skin (such as contact sports) if you have blisters on your skin
Complications of pemphigus vulgaris
Pemphigus vulgaris can lead to other problems, such as:
- blisters and sore patches becoming infected, which can cause life-threatening problems such as sepsis
- weight loss and malnutrition because of pain when eating and drinking
- tooth decay and gum disease because it can be painful to look after your teeth and gums
- pain during sex and pain when peeing or pooing (if your genitals or anus are affected)
You'll have regular check-ups to look for these problems and may be referred to other specialists (such as a dietitian) if needed.
Urgent advice: Ask for an urgent GP appointment or get help from NHS 111 if:
- your blisters or sore patches are very painful or feel hot
- there is yellow or green pus coming from your blisters or sore patches
These are signs of an infection, which needs to be treated quickly.
You can call 111 or get help from 111 online.
Causes of pemphigus vulgaris
Pemphigus vulgaris is caused by a problem with the immune system, which is the body’s defence against infection.
Instead of attacking germs, something goes wrong with the immune system and it attacks the skin by mistake. This damages the skin and causes blisters to appear.
It’s not clear why this happens. It’s not passed on in families and it’s not caused by an infection, so it cannot spread to other people.
Support if you have pemphigus vulgaris
Living with pemphigus vulgaris can be very difficult.
As well as support from your care team, it may help to get information and support from groups and charities such as:
- Pemphigus Vulgaris Network – a UK support group for people with pemphigus vulgaris
- PEM Friends – a UK support group for people with pemphigus vulgaris and related conditions
- International Pemphigus and Pemphigoid Foundation – a global support group for people with pemphigus vulgaris and related conditions
Page last reviewed: 30 May 2022
Next review due: 30 May 2025